Top 9 Cannabinoids and What Their Effects Are on the Body
Cannabis has long been celebrated for its therapeutic and recreational effects, but it’s important to recognize that not all cannabis is the same.
Cannabinoids are the active compounds in cannabis, and there are over 100 different types, each with its own set of effects.
Some cannabinoids are more widely known than others, and their individual properties can significantly impact how cannabis affects the human body.
Understanding the role of each cannabinoid can help guide consumers and medical professionals in choosing the right cannabis products for specific therapeutic purposes.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 9 cannabinoids, detailing their effects on the body and how they interact with the ECS to produce their therapeutic benefits.
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids naturally occur in cannabis and are similar to the endogenous cannabinoids created in the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of our bodies.
These cannabinoids created in plants like cannabis are called phytocannabinoids, and the body can use these to substitute and make up for the lack of endocannabinoids in the body.
These endocannabinoids produced in the body help promote homeostasis, which regulates the immune system and internal health of the body.
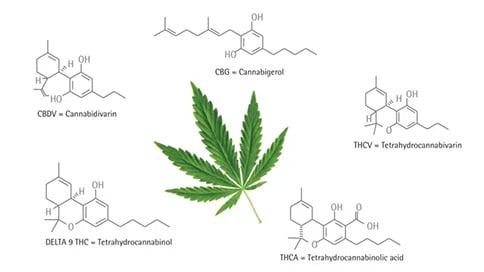
Credit for photo:https://www.technologynetworks...
How do Cannabinoids Work?
Despite millennia of use, it wasn't until fairly recently that we discovered the source for the effects of cannabis on the body.
In the 1960s and 70s, research into cannabis led to the discovery of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). As research continued, it was discovered that cannabinoids bind to receptors throughout the brain and body. These receptors came in two different classes. CB-1 and CB-2.
CB-1 is the most common receptor found in the central nervous system.
CB-2 is the most common receptor in the body's peripheral nervous system.
Cannabinoids interact with receptors in a similar way to other chemical compounds in the body.
They act as a key would in a lock. They bind to the receptors, which contain enzymes that allow the cannabinoids to be broken down and unlock the effects.
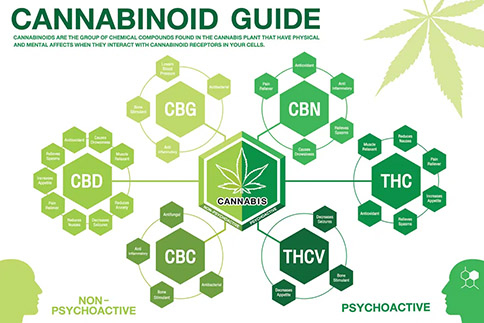
Top 9 Cannabinoids and what their effects are on the body
Several cannabinoids have been identified, and some of them have very different effects which match with the type and location of the receptors they interact with.
The two most commonly known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD); however, the number of cannabinoids and cannabinoid acids goes far beyond that.
Let now take a look at the ten most common types of cannabinoids and acids, as well as their effects and benefits for your health:
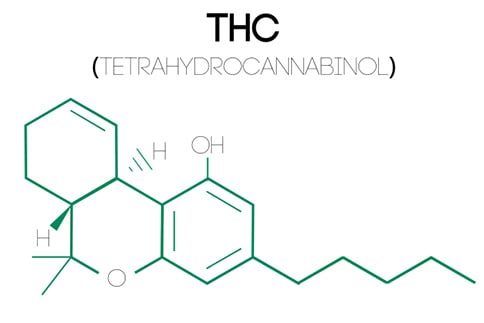
1. THC/Tetrahydrocannabinol
THC, or Tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in the resin secreted by the glands of the cannabis plant.
It is the compound responsible for the characteristic "high" that users experience when consuming marijuana.
THC interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, specifically binding to CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system, which leads to various effects, including altered perception, mood changes, and heightened sensory experiences.
Properties
- Reduces nausea
- Muscle relaxant
- Antioxidant
- Relieves spasms
- Increases appetite
- Pain reliever
- Glaucoma pressure relief
Used to treat
- Withdrawal symptoms
- Digestive issues
- Nausea
- Glaucoma
- Anxiety
- Potential anti-tumor properties
Credit for photo:https://cbdoilreview.org/cbd-c...
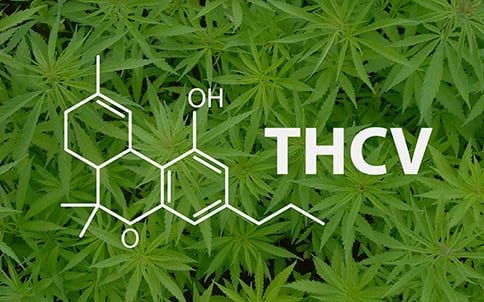
2.THCV/Tetrahydrocannabivarin
THCV is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis, known for its appetite-suppressing and stimulating properties.
Unlike THC, which is commonly associated with sedation, THCV is more energizing and can enhance focus and clarity.
This has led to it being dubbed “diet weed” and “weeder all” due to its potential to curb appetite and increase energy.
Properties
- Appetite-suppressant
- Seizure reduction
- Bone stimulant
Used to treat
- Metabolic disorders
- Neuropathy
- Multiple sclerosis
3. CBN/Cannabinol
CBN is a mild to non-psychoactive cannabinoid found mostly in aged cannabis.
It is often misunderstood as a potent sleep aid, though it shows more effectiveness when combined with other cannabinoids in full or broad-spectrum formulations.
CBN is typically present in low concentrations (less than 1%) in most cannabis strains.
Properties:
- Relieves spasms
- Pain reliever
- Sleep aid
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antioxidant
Used to Treat:
- Asthma
- Sleep disorders
- Pain relief
- Inflammation
4. THCA/Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid
THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) is the most prominent cannabinoid found in fresh, undried cannabis plants.
It is the acidic precursor to THC, and it becomes psychoactive only when heated through a process known as decarboxylation.
This transformation occurs during smoking, vaping, or cooking cannabis, turning THCA into THC, the well-known psychoactive compound.
While THCA itself does not have the intoxicating effects associated with THC, it still boasts a wide array of therapeutic properties that make it valuable in the medical cannabis community.
Properties:
- Bone stimulant
- Antibacterial
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antifungal
- Lowers blood pressure
- Inhibits tumor cell growth
Used to Treat:
- HIV/AIDS
- Inflammation
- Pain relief
- Tumor growth prevention
5. CBD/Cannabidiol
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the most well-known non-psychoactive compounds found in cannabis.
Unlike THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD does not induce a "high" and is often marketed for its potential therapeutic benefits.
While many people use CBD products for pain relief, anxiety reduction, and improved sleep quality, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is still evolving.
Additionally, some CBD products may contain trace amounts of THC, which can have psychoactive effects and be potentially harmful.
Properties
- Antidiabetic
- Antipsoriatic
- Bone stimulant
- Inhibits tumor cell growth
- Lupus and arthritis relief
- Reduces artery blockage
- Relaxes veins
- Minimizes organ rejection
Used to treat
- Cancer
- Arthritis
- Lupus
- Diabetes
- Tumor growth

6. CBG/Cannabigerol
Cannabigerol acid (CBGA) is a precursor compound in the cannabis plant and plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of many other cannabinoids, including CBG (Cannabigerol), THC, and CBD.
Although it is not as well-known as other cannabinoids, CBGA has demonstrated several therapeutic properties that make it an important component of the cannabis plant.
Properties
- Cardiovascular Health
- Better Metabolism
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antioxidant Effects
- Stress Management
Used to treat
- Cardiovascular Disorders
- Metabolic Disorders and Digestion:
- Inflammatory Conditions
- Oxidative Stress and Aging
- Stress and Anxiety
7. CBC/Cannabichromene
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis.
It does not produce the psychoactive effects associated with cannabinoids like THC, but research suggests that it may play an important role in the therapeutic effects of cannabis.
CBC is known for its strong anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to interact with various receptors, including TRP cation channels, to produce pain-relieving and inflammation-reducing effects.
While CBC is one of the lesser-known cannabinoids, it is thought to contribute significantly to the overall medicinal benefits of cannabis
Properties
- Bone stimulant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antifungal
- Lowers blood pressure
- Relaxes veins
Used to treat
- Chronic pain
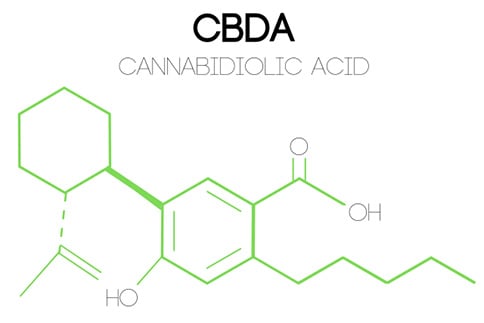
8. CBDA/Cannabidiolic Acid
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in the raw, unheated cannabis plant.
It is the acidic precursor to cannabidiol (CBD), much like how THCA is the precursor to THC.
CBDA is non-psychoactive and undergoes decarboxylation when heated, converting it into CBD.
Properties
- Bone stimulant
- Antibacterial
- Anti-inflammatory
- Lowers blood pressure
Used to treat
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea/Vomiting (CINV)
- Infections
- Inflammation
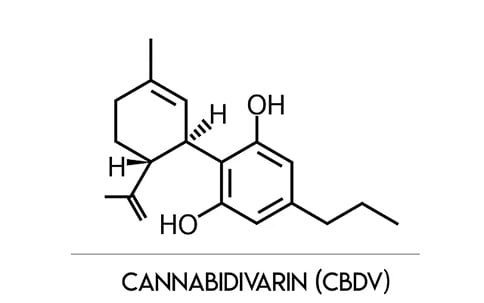
9. CBDV/Cannabidivarin
Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis.
Unlike THC, it does not cause the euphoric “high” typically associated with cannabis use.
Structurally similar to cannabidiol (CBD), CBDV has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic benefits, especially in neurological health.
It is most commonly found in indica strains, particularly landrace indica varieties, and strains with low tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content.
Properties
- Anti-epileptic
- Neuroprotective
- Anti-inflammatory
Used to treat
- Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
- Neurological Disorders
- Inflammatory Conditions
In Conclusion
Cannabinoids offer a wide array of therapeutic potential that is becoming increasingly recognized in the medical field.
From the psychoactive properties of THC to the non-psychoactive benefits of CBD, CBG, and others, each cannabinoid interacts with the body in unique ways.
Whether it’s helping to manage pain, reduce inflammation, alleviate anxiety, or promote better sleep, cannabinoids provide diverse solutions for improving overall health and well-being.
Read more: Does More Water Mean Less THC for Recycling Bong Vaping?
